July – Sep 2022
This report highlights the achievements of PIND’s program interventions in the Niger Delta from July – September 2022 (Quarter 3, 2022), and provides relevant information about program management, lessons learned, and plans for the next quarter. The report demonstrates how PIND is driving change to ensure broad-based economic growth in the Niger Delta.
PIND’s activities are designed to promote and sustain a culture of learning and adaptation, build a process where evidence plays a significant role in determining policy direction and interventions in economic development, peace building, advocacy, and capacity building of both government institutions and civil society in the Niger Delta.![]()
DOWNLOAD FULL REPORT
With PIND’s market development projects continuing to demonstrate progress towards widespread change, 28,213 farmers and agricultural entrepreneurs were reached with information and services on agriculture and business best practices and efficient technologies in the crop and non–crop sectors. Cumulatively 55,602 farmers/MSMEs (40% women) have been reached so far in 2022.
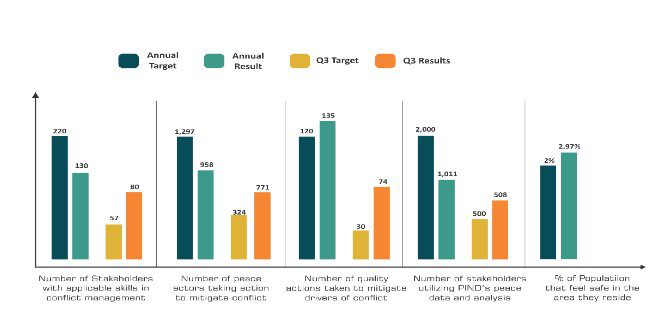
PIND incentivized MSMEs and participating farmers to invest ₦8.43 billion to implement good agricultural practices, technological innovations, purchase inputs and undertake other capital expenditures. A total of ₦11.05 billion has been leveraged so far in 2022 (₦7.02 billion: Equity and ₦4.03 billion: debt).PIND continued to play a significant role in driving the market for low–carbon, low–cost solutions that offer high–quality energy access to coastal communities. In Q3, 2022, a PIND–supported partner, A4&T Limited benefitted from the Rural Electrification Agency (REA)–promoted national rural electrification fund (REF2) project at Iyansan, Ondo State, which attracted a blend of public and private sector investment in the form of a ₦100m public investment facilitated through the REA, matched by a ₦45m contributory investment from A4&T. As a result, 438 households (2,772 persons) and 144 new businesses were connected to electricity in Iyansan community in Ondo State. Cumulatively, 624 businesses and 1,188 households have been given access to electricity goods and services, so far in 2022. Also, ₦441.875 million was recorded as financial benefits accruing to businesses and households accessing clean energy, facilitated by PIND.In the GMoU communities, PIND continued its support to demonstration activities of the usefulness of chorkor ovens. PIND, in collaboration with the Nigeria Institute for Oceanography and Marine Research (NIOMR) carried out capacity–building training for 100 fisher folks across five GMOU communities: Awoye, Molutehin, Gbagira, Odofado, and Messe in Ondo state. Participants were exposed to safety measures in their fishing activities, appropriate use and maintenance of their fishing gears, and other sustainable fishing practices such as the protection of breeding sites for sustainable fishing activities. Also, PIND continued to provide support to the Service Providers, Masons, and fabricators whose capacities have been built to drive the uptake of chorkor ovens to improve the efficiency of fish processors in the Niger Delta region and facilitated the adoption of 40 chorkor ovens in Ajudaibo, Mandagho, and Ogidigben GMOU communities in Delta state. This makes the total number of chorkor ovens adopted in 2022 so far to be 75.PIND produced 18 conflict reports including 14 weekly conflict briefs, a quarterly conflict tracker (2022 Q3), published its perception of safety and security report, and two case studies on data–driven and community–initiated conflict prevention and peacebuilding interventions, in its drive to continually create situational awareness, update stakeholders and catalyze mitigative responses, this quarter. Also, PIND assisted 771 peace actors to constructively resolve emerging conflicts in various communities in the Niger Delta. This led to 74 quality actions1 being taken to mitigate conflict in different locations across the region. Cumulatively, 958 peace actors have taken action to mitigate conflict, utilising 135 quality actions, so far in 2022.PIND produced 15 conflict reports including 13 weekly conflict briefs and a special policy brief on peace and security impact of illegal artisanal oil refining in the Niger Delta, to create situational awareness, update stakeholders and catalyze response actions, this quarter. Also, PIND assisted 136 peace actors to constructively resolve emerging conflicts in various communities in the Niger Delta. This led to 13 quality actions1 being taken to mitigate conflict in different locations across the region.PIND continued its work to ensure access to arable land in the Niger Delta. In Edo State, PIND facilitated collaboration between the office of the governor of Edo state and the state ministry of agriculture and natural resources to ensure alignment between the action plan produced by the land review committee and MDAs in the State. Also, PIND continued engagements with State governments in the Niger Delta to influence public spending on development projects that benefit the people of the region. In Cross River State, PIND’s engagements hinged on the alignment of State fiscal actions with the Cross-River State Growth and Development Strategy (GDS), facilitated by PIND.
In line with its effort to diversify and expand its funding base, PIND continued engagements with potential partners to explore new opportunities across its program areas. PIND submitted three proposals – a $400,000 grant request to Ford foundation, aimed at building the capacity of selected communities involved in the PIA process; another proposal in collaboration with Worldfish to implement the $1,300,000 Climate–Resilient Aquaculture Systems for Africa (CASA) project under the NANMO in Nigeria; and a third, in collaboration with UNICEF for the £1,500,000 Girls Education Skills Partnership Challenge Fund for skills development for young women across Nigeria. PIND also coordinated two Business Development & Strategy meetings (PIND–NDPI subcommittee and Board Committee) to provide a mechanism for monitoring and reviewing the BD strategies, and support the attraction of diverse sources of funding for PIND’s sustainability.By amplifying PIND’s communications this quarter, 2,079,002 people gained new or increased awareness about PIND, through its various platforms: newsletters, social media, website, email inquiries, forums and traditional mainstream media. Also, PIND garnered 34 positive media mentions of its work and activities and attracted 24 public endorsements from stakeholders who interacted with its content on the website, newsletters, and social media posts during the review period.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
In Q3 2022, the Market Systems Development (MSD) Project continued its work with service providers and other key market actors (fabricators, agricultural–input and equipment companies, farmers’ associations, financial institutions, etc.) to improve the performance of farmers.
As a result, 28,213 new farmers and enterprises (direct– 16,763; indirect–11,450) were reached with information and
knowledge on best practices and efficient technologies, representing a 156% performance against the quarter’s target of
18,080. Cumulatively, 55,602 farmers/MSMEs (40% women) have participated in economic activities so far in 2022,
achieving 80% of the annual target of 69,500. The program undertook an outcome monitoring exercise of its activities. This was to determine the extent of behavior change by farmers who participated in the various trainings provided by service providers, and the level of farmers’ adoption of the improved practices introduced by PIND. The exercise revealed an average adoption rate of improved
practices of 85% (49,640 adopting farmers/MSMEs) across all sectors, which was used in estimating the impact of all the
interventions as of Q3, 2022, as summarized below.
- Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: The number of adopting farmers/MSMEs who earned increased income on the MSD project in 2022 so far, was estimated to be 30,760, representing 67% of the annual target of 46,055 farmers/MSMEs.
- Change in the income of farmers: Consequently, the net attributable income change (NAIC) of these farmers/MSMEs on the project was estimated to be ₦16.34 billion, representing 97% performance of the 2022 target of ₦16.85 billion.
- Value of investment leveraged: PIND leveraged additional investments worth ₦11.05billion11(41% were investments by women) from participating farmers/MSMEs on the MSD project, as of Q3 2022. This performance represents 121% of the 2022 annual target of ₦9.3billion.
- Number of jobs facilitated: The project facilitated the creation of 8,771 full–time equivalent (FTE) jobs12, by adopting farmers/MSMEs, representing 77% of the 2022 target of 11,330.
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: AQUACULTURE
During the review period and in line with the planned activities to graduate this sector , PIND deepened its work with the network of aquaculture service providers to further create awareness on the use of quality inputs and to build the capacity of fish farmers and processors, to access funds for equipment and input purchase, particularly in the GMOU communities. PIND also continued its support to selected hatchery operators to produce and promote quality fish seeds for farmers, in addition to overseeing and tracking the expansion of the training on good pond management and business practices to more farmers and processors, through service providers and input companies in the region. Consequently, PIND reached 885 new farmers/processors (289 females) in Q3 and 4,218 (42% females) cumulatively in 2022.
The outcome monitoring exercise revealed an adoption rate of improved practices of 87% for the aquaculture sector Using this, the aquaculture estimated impact results as of Q3 2022 are summarized below:
o Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: The number of farmers/MSMEs with increased income was estimated to be 1,774 representing 89% performance of the annual target of 2,000 farmers/MSMEs.
o Change in the income of farmers: This is the additional income from the adoption of improved practices relative to traditional practices. The net attributable income change for aquaculture farmers/MSMEs as of Q3 was estimated to be ₦1.28 billion, representing 122% performance of the 2022 target of ₦1.05 billion.
o Value of investment leveraged: This is the cost of adopting improved fish–pond practices and associated technology to increase productivity. The net estimated investment by the aquaculture farmers/MSMEs in adopting improved fish–pond practices/technologies in their farms was ₦3.37billion (42% were investments by women), representing 225%13 performance of the 2022 target of ₦1.5billion.
o Number of jobs facilitated: This is the combination of additional full–time employment and temporary paid man–hours engaged by aquaculture farmers/MSMEs. As of Q3, the estimated net jobs (full–time equivalent) created by the adopting farmers/MSMEs was 1,629, representing 192% of the 2022 target of 850.
Learn more
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: CASSAVA
This quarter, PIND continued to expand its activities on productivity improvement, working with new and existing partners across the region, by providing support to partners to strengthen relationships and linkages with farmers to ensure access to agricultural information, and quality inputs including stems, fertilizer, and CPPs required for their production. These partners conducted training programs and established demonstration plots on good agronomic practices across the region, reaching 2,392 direct farmers (1,349 females) this quarter and 20,083 farmers (direct and indirect. 61% females) cumulatively, representing 80% of the 2022 target of 25,000.
The outcome monitoring showed that 13,842 indirect farmers copied from the direct adopters in 2022. Also, the exercise revealed an adoption rate of 99%, which was used to estimate the impact results for the cassava sector as summarized below:
o Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: The number of cassava farmers with increased income was estimated to be 8,451 for direct participating farmers only. Indirect farmers with increased income will be reported in Q4 after verification of the copier’s adoption levels which is underway.
o Change in the income of farmers: This is the additional income by the farmers who adopted improved practices on their farms and earned increased incomes. The net attributable income change for adopting farmers as of Q3 was estimated to be ₦3.46 billion. This represents 72% performance of the 2022 target of ₦4.80 billion.
o Value of investment leveraged: The investment leveraged is the difference in production cost between farmers reached and farmers yet to be reached with training and quality inputs. The net estimated investment by cassava farmers in adopting good agronomic practices (GAP) in their farms was ₦562.88 million (61% were investments by women) as of Q3 2022. This represents 93% of the 2022 target of ₦605 million.
o Number of jobs facilitated: Also, as of Q3, the estimated net jobs (full–time equivalent) created by the direct cassava adopting farmers was 561. The creation of full–time equivalent (FTE) jobs in cassava production is largely from the use of manual labor, rather than mechanization, by smallholder farmers for most farming activities such as land preparation, planting, and application of herbicides and fertilizer. Smallholder farmers cultivate small portions of land, in many cases smaller than one hectare, making the use of tractors, and other mechanical equipment uneconomical, except where farmlands are contiguous, and farmers are willing/ able to combine their resources to access mechanization.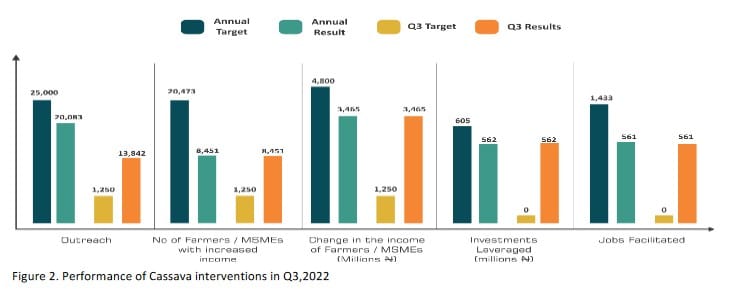
Learn more
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: COCOA
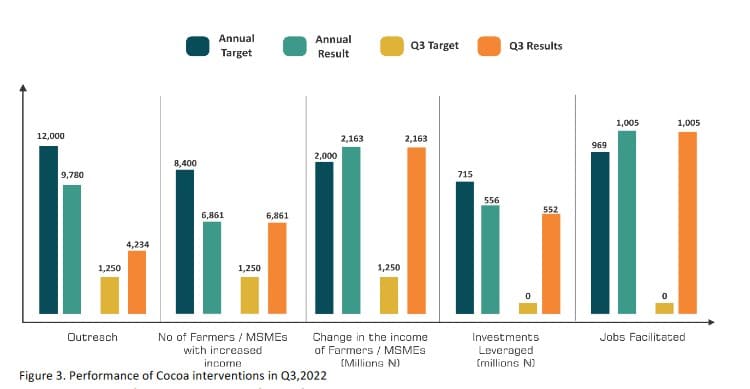
In 2022, PIND is supporting market actors to reach an additional 12,000 farmers with information on good practices, quality agro–inputs, and efficient technologies in the cocoa producing states. In the quarter under review, PIND supported export companies, input companies, nursery operators, and Farm Service Providers to organize training programs and demonstration activities to reach 4,234 new farmers. The number of farmers reached cumulatively as of Q3 2022, is 9,780 (25% females), representing 82% of the annual target of 12,000 farmers.
Findings from the outcome monitoring showed that about 70% of the 9,780 farmers who participated in the training and demonstration activities eventually adopted the improved practices, technologies, and innovations promoted by PIND, on an average of 2.45 hectares of cocoa farm per farmer. From the above, the estimated impact results for cocoa as of Q3 are summarized below:
o Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: The number of cocoa farmers with increased income was estimated to
be 6,861, representing 82% of the annual target of 8,400 farmers.
o Change in the income of farmers: This is the additional income from the adoption of improved agronomic practices such as pruning, spraying, fertilizer application, etc. relative to the traditional practices. The net attributable income change for adopting cocoa farmers as of Q3 was estimated to be ₦2.16 billion which represents 108% of the 2022 target of ₦2billion.
o Value of investment leveraged: This is the cost of adopting improved practices and associated technologies (i.e. mechanical pruners, mist blower, and fermentation boxes) to increase productivity. As of Q3, the net estimated investment by cocoa farmers in adopting improved practices/technologies on their farms was ₦556.25 million15 (25% were investments by women). This represents 78% of the 2022 target of ₦715 million by women.
o Number of jobs facilitated: As farmers adopt improved practices and technologies and expand production, they engage more labor to undertake various farm management activities such as land clearing, application of agrochemicals, pruning, harvesting, fermentation, drying, etc. As of Q3, the estimated net jobs (full–time equivalent) created by the adopting farmers was 1,005, representing 104% of the 2022 target.
Learn more
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: PALM OIL
Last year, PIND on–boarded one new seed producer and promoted the business finders’ model which led to 304 palm oil farmers purchasing and planting 274,825 seedlings in the region. PIND plans to onboard another seed producer and support it to increase its network of nursery operators to enable it to reach more farmers.
In the review period, PIND activities focused on working with intervention partners to expand intervention activities. PIND leveraged its relationships with oil palm Business Membership Organizations to onboard new farm service providers and lead farmers, to reach 1,562 farmers with information on BMP in the region. Also, activities were carried out to strengthen the relationship amongst value chain actors in the agricultural input industry, resulting in 86 farmers planting 102,163 improved oil palm seedlings. Cumulatively 11,408 farmers (29% females) have been reached so far in 2022, representing 76% of the 2022 target of 15,000 farmers.
Findings from the outcome monitoring exercise revealed that all the farmers and small processors reached, adopted the improved practices/technology promoted by PIND. The estimated impact results are summarized below:
o Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: 7,714 framers/MSMES were estimated to have increased their incomes as a result of the interventions promoted by PIND in the sector, so far in 2022. This represents 94% of the 2022 target of 8,165 farmers/processors.
o Change in the income of farmers: The net attributable income change for adopting farmers/MSMEs as of Q3, was estimated to be ₦5.14 billion, representing 106% of the 2022 target of ₦4.85 billion.
o Value of investment leveraged: The net investment leveraged by the sector from farmers adopting improved practices and technology, was estimated to be ₦1.37 billion as of Q3, representing 101% of the 2022 target of ₦1.35 billion.
o Number of jobs facilitated: As farmers adopt BMP and harvesting technologies, they engage temporary labor. As of Q3, the estimated net jobs (full–time equivalent) created by the adopting farmers was 802. This was 38% of the 2022 target of 2,100. This could be due to a reduction in labor resulting from the adoption of higher capacity mills with higher automation. Also, there seems to be a reduction in the number of field support workers engaged by the harvesters using mechanical adjustable harvesters (MAH) and Malaysian Knives (MK) as owners of farms are deploying more family unpaid labor in their harvesting of fresh fruit bunches (ffbs).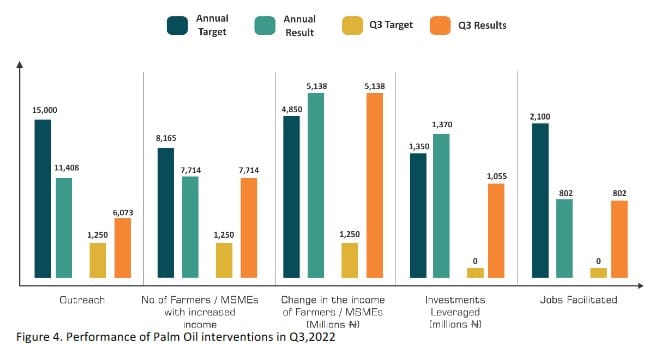
Learn more
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: POULTRY
A total of 18 training events were carried out during the quarter by 13 PSPs and 5 VLDs resulting in an outreach of 1,928 (718 females) farmers in Ondo, Edo, Delta, Bayelsa, Rivers, Imo, and Akwa Ibom states. Some of the farmers were supported with technical and business skills training, linkages to inputs (feed & vaccines), market, and finance. Cumulatively, 5,985 farmers (42% females) have been reached so far in 2022, representing 75% of the annual target of 8,000. With an adoption ration of 80% (from outcome monitoring), the estimated impact results for Poultry as of Q3 are summarized below:
o Farmers/MSMEs with increased Income: The number of poultry farmers with increased income was estimated to be 3,386 representing 70% of the annual target of 4,817 farmers.
o Change in the income of farmers: This is the additional income gotten by farmers trained by PSPs16, and adopting improved poultry practices, leading to a reduction in mortality rate, increased weight of birds, and resultant premium market prices. The net attributable income change of poultry farmers as of Q3 was estimated to be ₦1.61 billion representing 98% performance against the 2022 target of ₦1.65 billion.
o Value of investment leveraged: This is the additional cost for adopting poultry good practices such as improved feeds, biosecurity, modern feeders, vaccines, etc. to increase productivity. The investment leveraged was estimated to be ₦1.16 billion as of Q3,2022, representing 78% of the annual target of ₦1.48 billion.
o Number of jobs facilitated: As farmers adopt improved practices, technology and expand production, they engage more labor to undertake various farm management activities such as water provision ad–lib, cleaning cages, etc. As of Q3, the estimated net jobs (full–time equivalent) created by the adopting farmers was 1,673, representing 95% of the 2022 target of 1,758.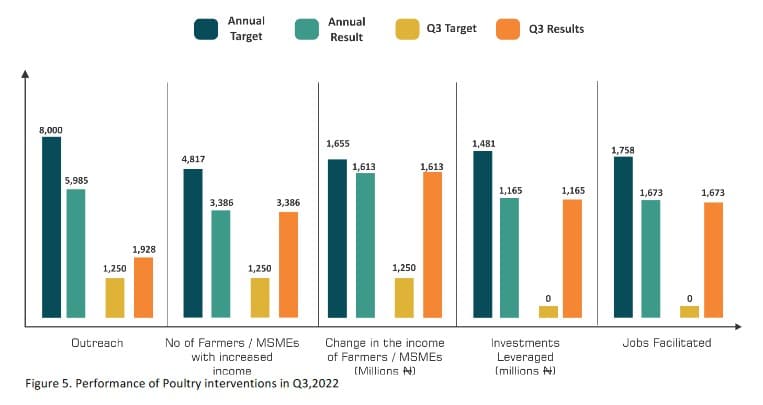
Learn more
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS: MSME DEVELOPMENT & LINKAGES
In Q3, nine BSPs trained and supported 1,251 MSMEs (496 women–owned) with services including: business management, business plan development, loan application, and linkages to finance through the CBN Agri–Business/Small and Medium Enterprise Investment Scheme (AGSMEIS) scheme and other MSME–friendly loan schemes. Cumulatively, 4,128 MSMEs have been reached so far in 2022, achieving 92% of the target of 4,500 for 2022. At an adoption ratio of 74%, the estimated impact results are summarized as follows:
o MSMEs with increased Income: So far in 2022, 59% of the micro–enterprises, and 89% of small enterprises who received business information, training, and access to new markets and funding opportunities, facilitated by PIND witnessed significant changes in their business performance. This translates to 2,574 MSMEs (2,197 micro, and 377 smalls,) with improved performance in 2022, achieving 117% of the target of 2,200 for 2022.
o Change in the income of MSMEs: So far in 2022, the net additional sales recorded by 74% of the outreach – those with new transactions, was ₦11.35 billion. Of this, ₦2.69 billion was net additional income (net profit of 23.7%), achieving 107% of the target of ₦2.5 billion for 2022.
o Value of investment leveraged (Loans– debt financing): Within the quarter, a total of ₦1.75 billion was accessed by 682 businesses, under the CBN AGSMEIS scheme. Cumulatively, BSPs have facilitated loans worth ₦4.03billion for the acquisition of new equipment and technology, expansion into new business lines, and to improve working capital, so far in 2022; and achieved 103% of the annual target of ₦3.5billion.
o Number of jobs facilitated: As enterprises expand by accessing new markets and funding opportunities, they engage more staff to support their increased business operations. An estimated 3,101 jobs were created by the 2,574 MSMEs reported to have experienced a significant increase in income in 2022. The 3,101 jobs facilitated is 75% performance against the target of 4,140 jobs for the year.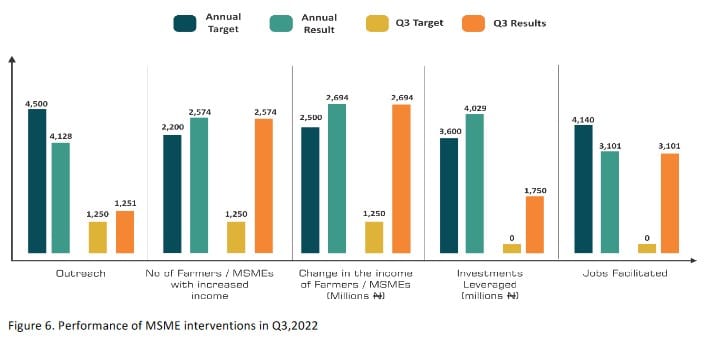
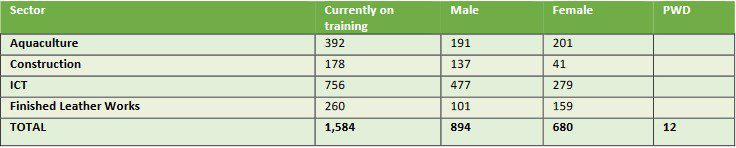
Learn more The total number of the trainees who have graduated from the NDYEP scale up program as of Q3 2022, is 1,196 (46% female, 4% PWD), thus achieving 83% of the 1,400 targets for 2022. In the review period, 175 additional participants enrolled in the NDYEP program, making the total number of youths participating in the NDYEP scale–up program so far in 2022, 1,168, across Abia, Akwa Ibom and Rivers States. In addition, 981 youths are undergoing training in Delta, thus 2,149 enrolled in the skills development for youth employment program across the four States. 565 of those who enrolled in 2022 graduated in Q3, with 1,584 youths remaining who are still being trained as outlined in the table below
 The PIND entrepreneurships training is a post skill training program designed to equip the all YEP participants who have completed their skill training with requisite skills to own their businesses. The entrepreneurship training/ post training enterprise development support was conducted in July 2022, for past Delta Youth Employment program in Warri and Asaba, Delta State.
The PIND entrepreneurships training is a post skill training program designed to equip the all YEP participants who have completed their skill training with requisite skills to own their businesses. The entrepreneurship training/ post training enterprise development support was conducted in July 2022, for past Delta Youth Employment program in Warri and Asaba, Delta State.
The entrepreneurship training was conducted in line with the approved CBN curriculum for entrepreneurship programs and successful participants were certified and assisted to develop fundable business plans. The participants were also guided to complete online registration on the CBN or NIRSAL platforms. As part of the post training support, information and guidance are being provided on access to loans and other facilities available from government agencies and financial institutions. Also, a one-day sensitization/orientation was conducted for participants and exposed them to opportunities for entrepreneurship in the various sectors. Of the 337 youths who were invited for the training, 258 registered while only 227 successfully completed the training; these were 154 from Warri and 73 from Asaba including 122 women. Some of the trainees who couldn’t complete the training sited economic reasons for failure to attend or complete the training. Post training mentorship is continuing to support all emerging enterprisesThe coastline rural communities in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria suffer poor rural electrification, with many of the communities not having access to regular electricity supply to power basic economic assets and household needs, leading to reduced economic activities. Expectations for connection to the National grid anytime soon are unlikely due to high-cost implications and the difficult terrains. Since 2018, PIND has been addressing this gap through alternative and affordable off-grid solutions, capable of targeting not only basic energy needs (i.e lighting and cooking energy), but also productive use of energy at both household and rural enterprise levels (such as used in barber shops and beauty salons).
PIND’s Access to energy program had an outreach of 2,852 in Q3 2022. These are 2,772 persons across 144 businesses and 438 households now enjoying access to electricity from a newly energized community at Iyansan, a riverine community in Ondo State. Also, 30 rural businesses across GMOU communities in Delta State benefitted from PIND–partner funding towards the acquisition of electricity productive–use–equipment. In addition, 50 women participated in ‘a woman for energy jobs’ training. Cumulatively, the number of people provided with clean energy so far in 2022, is 7,752, comprising 624 businesses and 1,188 households.The highlight of PIND’s scale up activities in electricity access for Q3 2022 is the partner–led ₦145million 100kWp mini grid at Iyansan community in Ondo State. This Rural Electrification Agency (REA) promoted national rural electrification fund (REF2) project at Iyansan, Ondo State attracted a blend of public and private sector investment in the form of a ₦100m public investment facilitated through the REA which was matched by a ₦45m contributory investment from A4&T Limited. Through these leveraged funds, a total of 438 households and 144 new businesses were connected to electricity in Iyansan community in Ondo State. This has facilitated electricity access to 2,772 persons through investment made by the PIND partner – A4&T Power Solutions limited.
Relatedly, optimizing revenue generation and the utilization of electricity towards enterprise are two key objectives of the A2E drive for both partner mini grid operators and communities. To this end, PIND has continued to provide technical assistance towards optimizing the performance of the various community minigrid intervention projects. Through such continuous mentoring in Q3 2022, BeingCost limited (BCIS) benefited from a Nigeria Off Grid Market Acceleration Program (NOMAP) pilot to fund mini–grid companies to support the productive use of electricity in newly electrified communities. BCIS limited’s operations attracted private investor funds to the tune of ₦20m to support 30 rural businesses across Gbokoda, Kpokugbene and Ogbimbiri (3 GMOU communities) towards acquiring productive–use equipment at concessionary rates. For the mini grid developer, this program is projected to have an impact on electricity consumption and revenue generation, while the community beneficiaries will be able to create new jobs and experience
improved livelihood.Following the commissioning of two RDC–Funded 20kW energy cabins at Awoye and Odofado (two GMOU communities) last year, PIND and Morgan Smart development foundation undertook a joint assessment of the impact of energy access on these two communities in Q3, 2022. The assessment revealed that ₦258,958.33 was recorded as financial benefits accruing to users of the two mini grids since the commissioning of the solar mini grid in these communities. In addition to these, the study also showed that as a result of having access to electricity from the energy cabin 14 MSME’s across Awoye and Odofado invested ₦3.73 million towards expanding their businesses, while 17 Full time Jobs were created by some of the beneficiary MSMEs across the two communities between January and September 2022.
Cumulatively ₦441.875 million was recorded as financial benefits accruing to businesses and households accessing clean energy, facilitated by PIND, so far in 2022. This is made up of costs savings (₦13.82 million) resulting from reduced or discontinued use of generators for households and businesses, and increased incomes (₦428.05million) from improved service offerings for businesses. Financial benefits recorded are for users of energy cabins connected for a minimum of 9 months, with the understanding that sufficient time is required for benefits to be seen. As such the benefits captured here are for users connected in 2021 and before, for benefits accrued in 2022 only. As such benefits for new users reported/ connected so far in 2022 have not been recorded. Also, 26 cumulative FTE jobs were recorded as at Q3 2022.Partnerships are at the core of energizing coastal communities and as part of the efforts to steer access to energy solutions in unserved and underserved communities, PIND supported 3 clean energy businesses (Darway Coast, ETIN Power and Oghosa Limited) towards originating and partnering three riverine communities in Delta, Bayelsa and Edo states on renewable energy projects. These partnerships are poised to deliver commercial electricity connections for businesses and households in these communities for businesses as well as other first–time users.
In Q3 2022, PIND also established new partnerships with PODER Green consulting limited (A training partner within the GIZ training coalition network) on a “women for energy jobs” collaborative activity. Through the collaboration, PIND supported the identification and convening of stakeholders and market actors for a capacity development program to train 50 women in the Niger Delta as part of a national cohort. This activity will facilitate training that will see up to 50 Niger Delta women identified and trained in solar entrepreneurship jobs to support the technical manpower needs of the renewable energy sector in the Niger Delta over the next 1 year. Through this partnership, PIND will also be leveraging over ₦33 million through private sector investment towards creating FTE jobs for women. PIND’s intervention incentivized the promoters to look at Niger Delta participation across four states (Delta, Ondo, Rivers and Bayelsa) in a quasi–pilot activity. This is consistent with PIND’s effort to support the development of other A2E technology models and forms part of the year 2022 workplan.
PIND and AEAS Interventions in the Niger Delta
The AEAS project focuses on interventions in Aquaculture, Maize and Rice in Delta and Cross River States. Between April and June 2022, the Extension Activity identified and validated 11 additional MIPs, bringing the total list to 20 MIPs across the five target value chains it is intervening; nine of these MIPS are being promoted in Cross River and Delta State as shown below.
- Aquaculture: Stocking juveniles; Complementary feeding with Maggots and Duckweed
- Maize: Mechanized land preparation, Fall Army Worm control & management
- Rice: Mechanized threshing, Mechanized land prep with small equipment- power tillers (lowland rice)
- Maize & Rice: Use of improved seeds, optimum herbicide utilization for weed management, optimum fertilizer use
184 MSMEs (an increase by 5 MSMEs from the previous quarter) are partnering with the Extension Activity and receiving services to promote private sector extension in Cross River and Delta states. Of the 184 MSMEs, 85 MSMEs (an increase from 70 MSMEs in Q2) are commercializing the MIPs and provided extensions services to 20,838 SHFs, in the review period.
The 85 MSMEs provided extension services alongside sale of agricultural products and services. Also, nine of these MSMEs conducted demand stimulation and extension messaging campaigns in Cross River and Delta states on the use of juvenile and improved seeds in 6 LGAs, 2 in Cross River and 4 in Delta: Abi, Aniocha North, Isoko North, Ughelli North, Uvwie and Yakurr. To further reach farmers in rural communities with extension services and stimulate the adoption of MIPs, three MSMEs in Cross River State engaged and trained 23 private Agricultural Extension Agents (AEAs) to serve farmers in Abi and Yakurr LGAs in addition to the 80 that was engaged by 10 MSMEs in the last quarter.
In addition, an inputs credit model was introduced to partner MSMEs last quarter to meet the inputs needs of SHFs. Through this initiative, the first in–kind input credit worth $62,211(₦25.82 million) was disbursed in Cross River State by two MSMEs and CREIN, a micro finance bank to 359 SHFs.
The Extension Activity uses ICT to assist MSMEs in the promotion of MIPs and to support farmers in the adoption of improved practices and continued to promote WhatsApp and bulk SMS, and piloted community radio as platforms to enhance communications between MSMEs and farmers. During the reporting period, An MSME hatchery operator Bangadonose Ltd. in Calabar, demonstrated the knowledge gained from Extension Activity trainings using the ICT platforms (bulk SMS and WhatsApp group messages) to enhance communication and disseminate MIP messaging on the use of Juveniles to farmers within her network, where she has reached a total of 5,458 SHFs. Also, the Activity continued to collaborate with the Cross River State Agricultural Development Program (CRADP) to develop ICT–video enabled extension services platforms to demonstrate and disseminate the value and practice of MIPs to reach value chain stakeholders, by developing three additional MIPs videos (Use of small equipment for mechanization, Use of mechanized thresher and healthy nutrition focusing on healthy hygiene) during the reporting period; making a total of Eight videos developed for this initiative.
Following the capacity strengthening exercise of frontline healthcare and extension workers to promote nutrition–sensitive practices for farming households, last quarter, step–down trainings have been conducted by women in Agriculture, MSMEs, and health professional in Cross River and Delta states in Ikom, Yakurr Abi, Calabar South, Calabar Municipal, Oshimili South, and Ughelli North LGAs, as well as Ibusa, Asaba and Ughelli in Delta State, exposing a total of 1,370 farmers to the benefits of healthy Nutrition.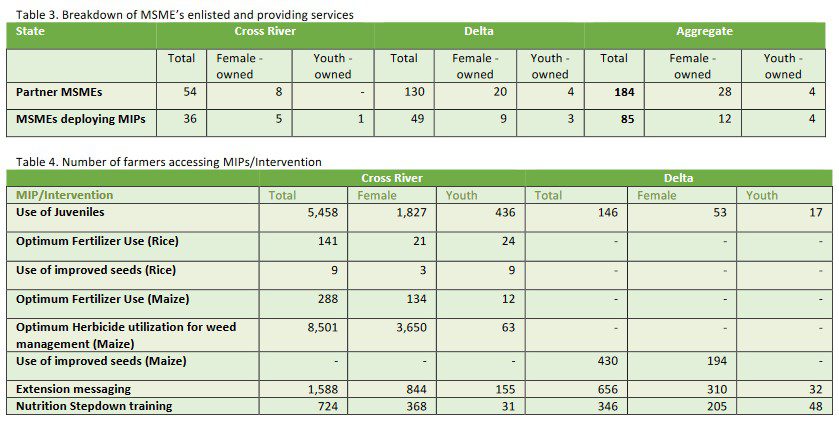
PEACEBUILDING
This section highlights key achievements of the Peace Building program in Q3, 2022
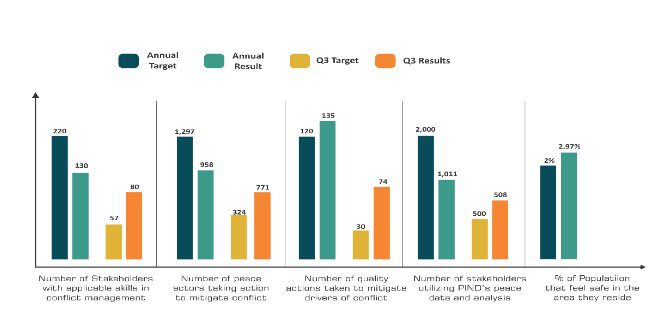
There was 66.8% increase in the number of conflict early warning incidents reports on the IPDU SMS platform during the quarter as 357 incidents were reported on the platform in Q3 compared to 214 incidents reported in Q2. From the early warning incidents reported on the SMS EWER platform, conflict alerts were generated and disseminated to 45 peace actors including the P4P Prevent committees for conflict update, situational awareness and preventive response. As such, PIND utilized conflict early warning, research and data analysis products to catalyze proactive responses to prevailing and emerging conflict risk factors and drivers of instability in the Niger Delta.
Policy Alert had used PIND’s Policy briefs, Peace map and Quarterly conflict trackers. During planning for community activities, we use them to identify if the community we’re going for advocacy/intervention is security risk free (a very valuable document). They are also very useful when writing our proposals, as we use it as a guide to know where to focus our intervention proposals.Sometimes, in our meetings, we refer to PIND’ Peace Map and Weekly conflict updates, and during communications across the states. We have a presence in most of the states in the Niger Delta and these reports provide us updates as well in decision making. We have used the updates provided in one of the editions (March 27 – April 2 on cult and gang violence) to plan advocacy in Delta & Bayelsa states.I use the Peace Maps, Quarterly conflict trackers, Weekly conflict updates for conflict analysis, research and learning. These are sources of data for my research and analysis.
TYPE OF CONFLICT ISSUE |
OUTCOME OF INTERVENTION |
| Communal Violence |
Unyime, a peace actor in Obon Obot community, Etim Ekpo LGA, is using his peace building skills to intervene in several community issues. In August 2022, there were violent clashes among members of Obon Obot, Uruk Atta II, Ikpe Annang, Atuai Eka Uruk Essiet, Ikot Eseh, Ikot Mkporikpo and Udianga Enem communities as a result of cult killings. This rendered many families homeless as their houses were burnt down. In September 2022, Unyime was part of the stakeholder engagements team. He facilitated a conflict resolution seminar to enhance behavioural and attitudinal change among community leaders and youths to resolve the conflicts. Some displaced families have started returning to their homes as the situation has returned to normalcy. |
TYPE OF CONFLICT ISSUE |
OUTCOME OF INTERVENTION |
| Cult violence and drug abuse |
Efe’s community is plagued with criminal activities, illicit drug use, and cultism. He worked with key stakeholders to engage the police, establishing community policing which have reduced the rate of criminal activities to some extent. As a member of P4P, he was part of the committee set up in August 2022 for a football competition between his community – Ojo-Urhobo, and Morobo community in Warri South LGA. Sports, especially football brings people together. They believe that with this football competition, they will bring the youths of the two communities together to promote peace and make them redirect the energy from drugs abuse or thinking about the next criminal activity. The competition ended in September 2022. |
 PIND also trained and commenced a mentorship program on fundraising and resource mobilization for 10 CAPABLE organizations and conducted an OCA and training for five BMOs in the sectors where PIND is intervening. A total of 16 individuals from 10 CAPABLE organizations across the region participated in a 3–day hybrid (physical & virtual) training and commenced the mentoring program which is scheduled to run till November 2022. The output of this mentorship is a minimum of one full proposal submitted by each organization to identified local and international funders. So far, five of the organizations have received support to prepare and submit initial applications: four to the AU Innovating Education in Africa and one to North America Association for Environmental Education. Two other organizations have prepared their drafts and are making improvements following feedback from the mentoring organization ahead of their application submission deadlines. Full–scale mentoring will commence in Q4 and each organization will be assigned two mentors to work with them to prepare and submit high–quality proposals to a range of local and international funders.PIND signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Niger Delta Affairs (MNDA) in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State, in September 2022. The MoU signing, held during the National Council on Niger Delta (NCND) meeting, solidifies PIND’s partnership with the MNDA to develop a regional peacebuilding infrastructure that would contribute to efforts to address conflict and security issues in the Niger Delta. As a significant player in the region’s development, PIND is a member of the technical committee of the NCND established in 2013. The technical committee’s role is to offer technical advice to the President and State Governors in the region on regional development and coordination issues.
PIND also trained and commenced a mentorship program on fundraising and resource mobilization for 10 CAPABLE organizations and conducted an OCA and training for five BMOs in the sectors where PIND is intervening. A total of 16 individuals from 10 CAPABLE organizations across the region participated in a 3–day hybrid (physical & virtual) training and commenced the mentoring program which is scheduled to run till November 2022. The output of this mentorship is a minimum of one full proposal submitted by each organization to identified local and international funders. So far, five of the organizations have received support to prepare and submit initial applications: four to the AU Innovating Education in Africa and one to North America Association for Environmental Education. Two other organizations have prepared their drafts and are making improvements following feedback from the mentoring organization ahead of their application submission deadlines. Full–scale mentoring will commence in Q4 and each organization will be assigned two mentors to work with them to prepare and submit high–quality proposals to a range of local and international funders.PIND signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Ministry of Niger Delta Affairs (MNDA) in Uyo, Akwa Ibom State, in September 2022. The MoU signing, held during the National Council on Niger Delta (NCND) meeting, solidifies PIND’s partnership with the MNDA to develop a regional peacebuilding infrastructure that would contribute to efforts to address conflict and security issues in the Niger Delta. As a significant player in the region’s development, PIND is a member of the technical committee of the NCND established in 2013. The technical committee’s role is to offer technical advice to the President and State Governors in the region on regional development and coordination issues.
PIND and MNDA shall be working with CSOs, donor communities, academia, security operatives, traditional rulers, and community influencers to establish a Technical Working Group (TWG) whose role will be to develop the mechanism behind the proposed peacebuilding infrastructure. The NCND formally approved the collaboration between PIND and MNDA mandating that work commence in earnest.PIND’s communication activities aim to increase its visibility by getting people to know about PIND, talk about it, and engage with it and its programs. They also aim to strengthen PIND’s reputation and attract target stakeholders to support its cause, partner with it, fund its programs and replicate its proven models.
In the review period, discourse on the digital media space continued to be dominated by the upcoming Nigeria 2023 general elections, insecurity, and migration of skilled workforce from Nigeria in search of greener pastures. PIND, keyed into the discourse by using relatable human stories to share critical messages of economic opportunities, peacebuilding, and enabling environment facilitated by PIND across multiple channels of communication: social media, newsletter, website, traditional media, forums, and knowledge products such as factsheets and reports. Via these channels, PIND’s brand messages reached a total of 2,079,002 target stakeholders, in Q3, 2022. The main highlight of the quarter was PIND’s participation in the Devex UNGA 77 fireside chat with the PIND Executive Director, Tunji Idowu. The platform opened PIND up more to the international space as new countries were seen viewing our website.
In Q3, 2022, PIND messages targeted at its stakeholder groups through the radio, TV, print, and online newspapers helped it to attain 34 positive mainstream media mentions across these channels, out of which nine were earned media mentions (third–party media mentions of PIND). The exposures reached an average of 1,196,691 people who became more or newly aware of PIND, its programs, models, and results. 34.7% of website visitors were youth between the ages of 25-34. A total of 5.77 million people has become more or newly aware of PIND via mainstream media channels so far in 2022.
PIND received 24 public endorsements from program participants, and the general public through various public media platforms. Cumulatively PIND has received 69 public endorsements so far, achieving 276% of its target of 25 for 2022. PIND also hosted and participated in eight forums where it shared relevant and useful lessons and evidence of its work to critical stakeholder groups to stimulate possible replication of the models and position.
PIND received a total of 71 email enquiries this quarter. Most of these enquiries sought information on access to PIND–promoted agricultural technologies, collaboration with PIND, media enquiry, academic research on PIND, and others (such as for either economic development or peace building matters). These enquiries indicate increased visibility and better positioning of PIND as a thought leader and go–to organization on issues of socio–economic development in the Niger Delta. In Q3 2022, 17,835 males and 11,618 females (39% of the total outreach) and 2,812 youths (10% of total outreach) benefitted from the various economic development interventions in the Niger Delta, targeted at improving their knowledge and practices; with an aim to increase their incomes and improve their livelihoods. Also 32 people with disabilities were reached through the Youth Empowerment Program (YEP) stakeholders’ engagement workshops.
Similarly, a total of 858 women (40% of the total beneficiaries), 1,297 (60%) men, 791 (37%) youths and 14 (1%) PWDs participated in various peacebuilding interventions including: conflict mitigation, forums on peace and stability, skills enhancements, and mentorships, for the advancement of sustainable peace in the region.PIND continued to engage potential partners to explore new opportunities across its program areas. PIND submitted three proposals as part of its drive to source grants to expand PIND’s program and project activities. PIND also coordinated two Business Development Strategy committee meetings (PIND/NDPI subcommittee and Board Committee). The aim of these meetings is to provide a mechanism for monitoring and reviewing the BD strategies, provide recommendations and support the attraction of diverse sources of funding to ensure PIND’s sustainability.
In addition, PIND continued to strengthen its thought leadership and position itself as a resource organization for the implementation of the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA), by supporting stakeholders in managing the processes that birth and administer the Host Communities Development Trusts as prescribed by the PIA. PIND’s partnership with Ford Foundation’s PIA Bridges Project, would bring different actors – companies, communities, NGOs, government, and others together to explore realistic models of community development.



