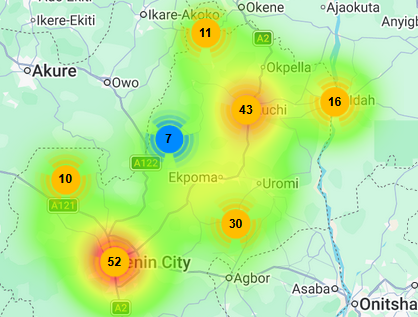
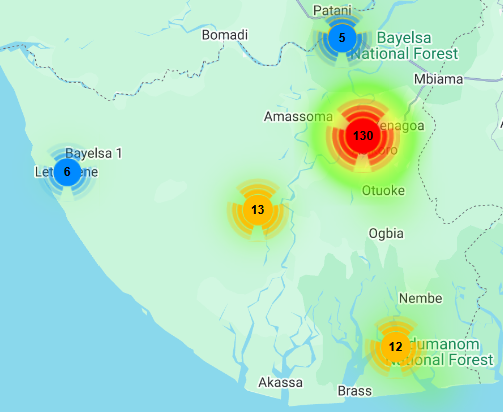
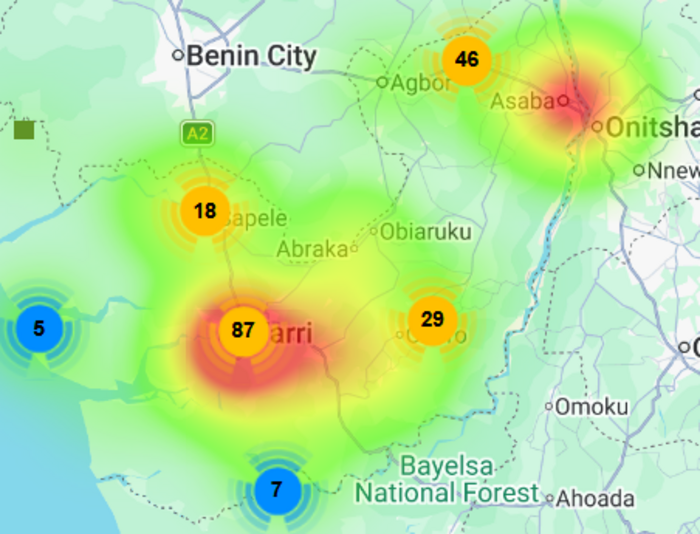
This special edition of the weekly update spotlights emerging threats to public health and human security in the Niger Delta with a focus on Monkeypox outbreak in the region. Monkeypox (Mpox) is a viral zoonotic infectious disease caused by a highly contagious Monkeypox virus. It can be transmitted through direct contact with infected persons, contaminated materials, or infected animals, including rodents and monkeys. Symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, weakness, swollen lymph, and skin rash. Mpox can spread from person to person and from animals to people. The current Mpox Clade 1 strain has reportedly caused fatalities in up to 10% of infected persons in previous outbreaks. According to epidemiological data from the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC), as of August 11, 2024, 39 confirmed cases and 786 suspected cases of Mpox have been reported in 19 States in Nigeria, including the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) Abuja, and all the nine States in the Niger Delta. According to NCDC’s Update on Mpox Outbreak, as of August 11, 2022, more than 32% (259) of all suspected cases were reported in the Niger Delta. Over 16% (132) of all suspected cases in the country were reported in Bayelsa and Cross River States.[embeddoc url="https://pindfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/dlm_uploads/2024/08/Niger-Delta-Weekly-Update-August-18-24-2024.pdf%22]![]()